How to Construct a 74x Leverage with Options Strategies
- When2Buy Official

- Jul 12, 2024
- 3 min read
I believe everyone is curious about how to scientifically design a leverage strategy to achieve over 500% profit, assuming a stock can only increase by 7% in a month. In this options strategy class, we will explore the Calendar Spread.
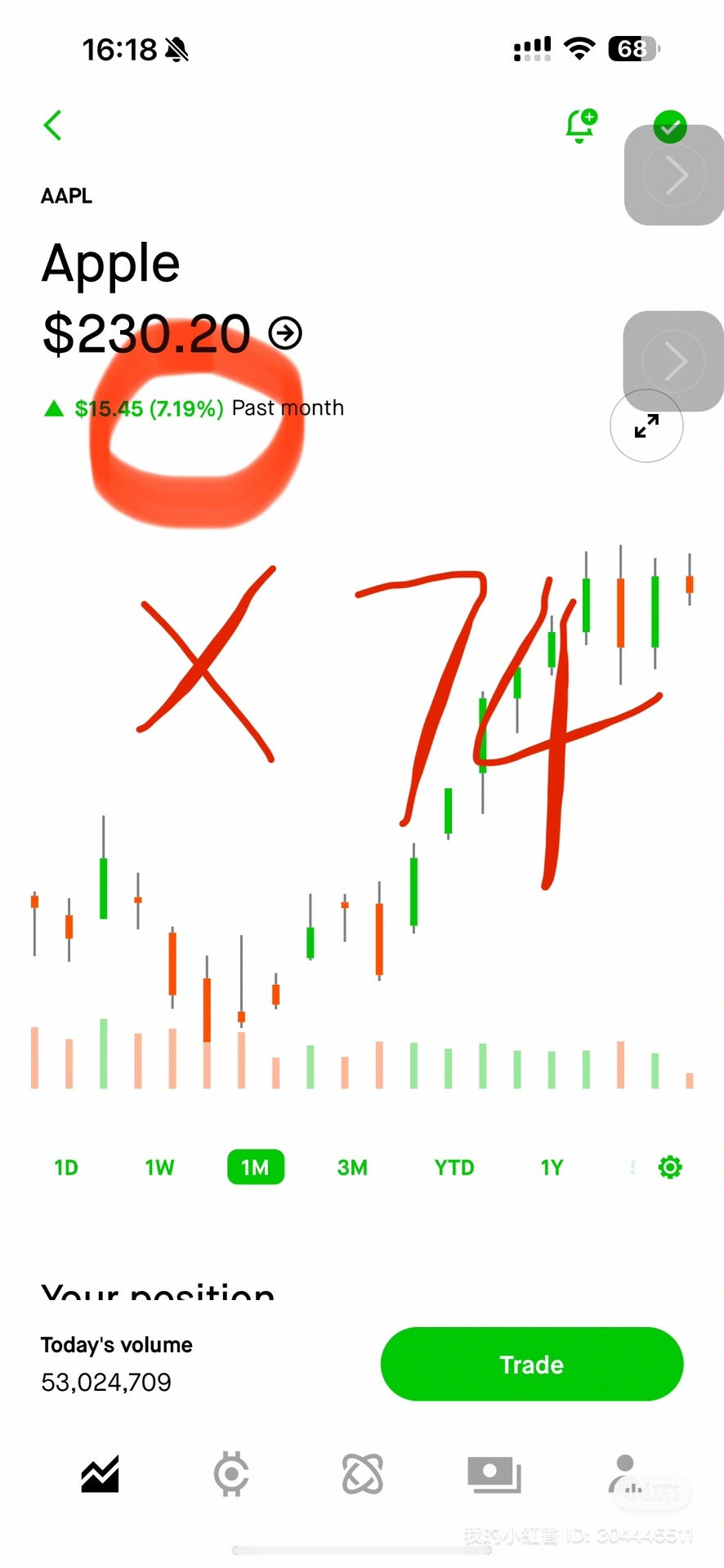
Today, as the market has closed, let's review the performance of this strategy on Apple stock over the past month.
Figure 1: Stock Trend
Figure 2: Calendar Spread Strategy
Figure 3: Call Strategy
Figure 4: Call Strategy Profit
Figure 5: AI Signal
By comparing the same $230 price level, the calendar spread has the following advantages over the $230 call option:
Lower Volatility: Its upward trend is even more stable than the stock itself.
Higher Total Profit: The profit is significantly higher than that of the stock and call option (7% vs. 91.12% vs. 524.61%). The principle is simple; we offset the cost with a short $230 option, and we make the most of both "price" and "time" (e.g., when the price reached $230 on 7/12).
The challenge lies in accurately predicting the price of the stock and being familiar with the construction of the calendar spread strategy. For instance, after receiving a series of AI buy signals on 6/12, I quickly calculated the potential upward space and set the target price at $230, using the historical trend to decide on this strategy. If you're interested, I can share some common methods for stock price prediction using technical analysis in the next session.
The calendar spread strategy is typically used for scenarios with small losses and one-time large gains. It often requires manual rollover adjustments, but with our carefully calculated strategy, the execution can yield the optimistic results mentioned above. If you have experience using this strategy, feel free to share and discuss in the comments.
Therefore, a well-designed options strategy can significantly enhance your investment efficiency. Interested students should not limit themselves to buying calls and puts. Proper use of multi-leg options like the calendar spread can make investments simpler and easier.
I highly recommend everyone to check out the book "Options as a Strategic Investment" by options investment master Lawrence McMillan. It was an eye-opener for me, correcting many of my previous options trading mistakes and teaching me new techniques (this book is especially recommended for those with a strong technical background as it is a bit challenging). It's a great resource for mastering various options strategies and equipping your investment toolkit to help you prosper.
Example of a Calendar Spread
Let's consider a practical example to illustrate how a calendar spread works. Suppose you are interested in Apple Inc. (AAPL), and the current stock price is $230. You anticipate that the stock will not experience significant price movement in the near term but will increase slightly over the next few months.
To implement a calendar spread, you could:
Buy a longer-term call option: Purchase a call option with a strike price of $230, expiring in three months (e.g., October).
Sell a shorter-term call option: Sell a call option with the same strike price of $230, but expiring in one month (e.g., August).
Here’s how it might look in detail:
Buy 1 AAPL October 230 Call for $5.00 per share.
Sell 1 AAPL August 230 Call for $2.00 per share.
Cost and Potential Profit
Net Cost: The net cost of the calendar spread is the difference between the premium paid for the longer-term call and the premium received for the shorter-term call. In this case, it would be $5.00 - $2.00 = $3.00 per share.
Breakeven Point: The stock price at which you break even is generally close to the strike price ($230), assuming no significant changes in implied volatility.
Outcome Scenarios
Stock Remains Stable: If AAPL stays around $230 by the first expiration date (August), the shorter-term call expires worthless, and you still hold the longer-term call.
Stock Increases Slightly: If AAPL increases slightly but remains close to $230 by the first expiration date, the shorter-term call may be exercised, but the premium collected offsets some of the cost. You still hold the longer-term call.
Stock Decreases: If AAPL decreases, both options may lose value, but the loss is limited to the net cost of the spread ($3.00 per share).
Advantages of the Calendar Spread
Lower Volatility Impact: The strategy benefits from the differing time decay rates of the two options, making it less sensitive to market volatility.
Potential for High Returns: The profit potential is substantial if the stock remains near the strike price at the time of the shorter-term option’s expiration.
By using a calendar spread, traders can effectively leverage their positions to benefit from stable or slightly increasing stock prices while managing their risk exposure. This strategy provides an excellent way to capitalize on time decay and volatility patterns in the options market.












Comments